Disentangled Motion Representation: Encoding Full-Body Avatars into Discrete Latent Spaces

Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Related Work
2.1. Motion Reconstruction from Sparse Input
2.2. Human Motion Generation
-
SAGE: Stratified Avatar Generation and 3.1. Problem Statement and Notation
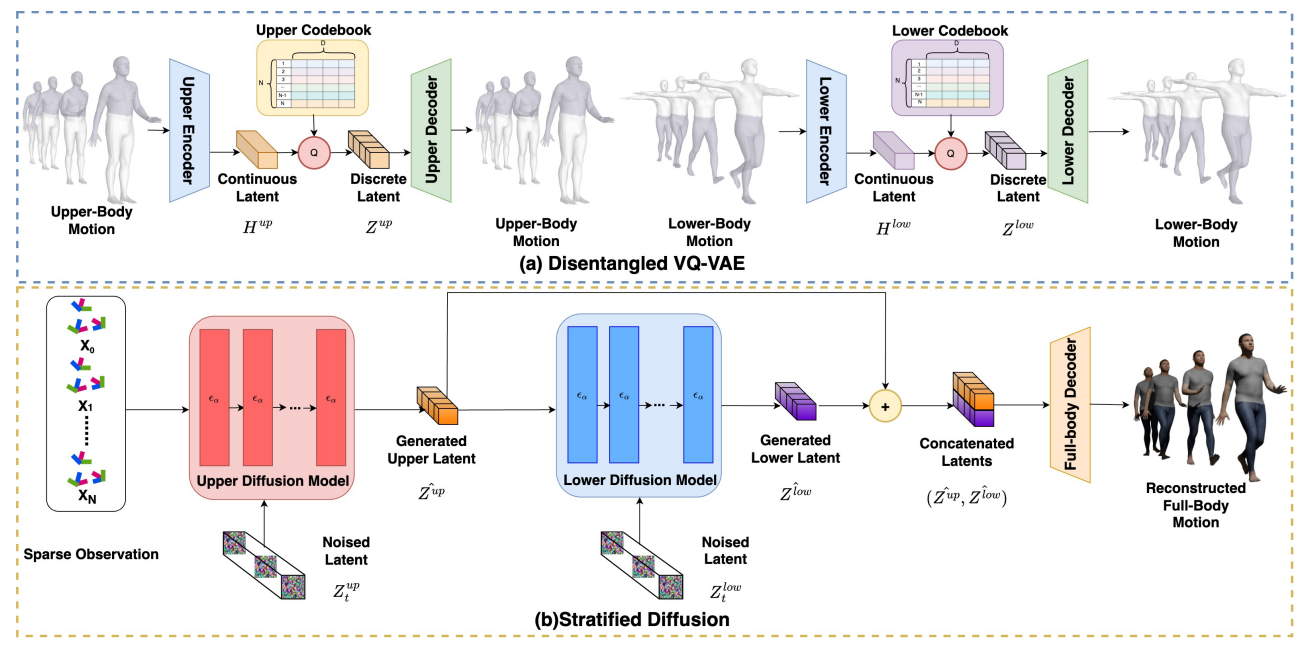
3.2. Disentangled Motion Representation
3.3. Stratified Motion Diffusion
3.4. Implementation Details
-
Experiments and Evaluation Metrics
4.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Quantitative and Qualitative Results
4.3. Ablation Study
-
Conclusion and References
\
Supplementary Material
A. Extra Ablation Studies
B. Implementation Details
3.2. Disentangled Motion Representation
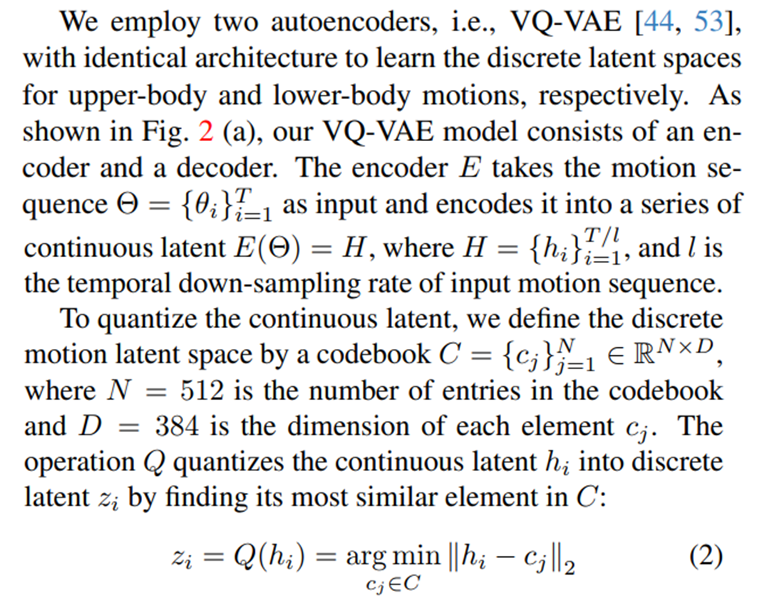
In this section, our objective is to disentangle full-body human motions into upper-body and lower-body parts and encode them to discrete latent spaces. This can effectively reduce the complexity and burden of encoding since each encoding takes care of only half-body motions.
\
\
\
Since continuous latent from all data samples share the same codebook C, all the real motions in the training set could be expressed by a finite number of bases in latent space.
\

\
:::info
Authors:
(1) Han Feng, equal contributions, ordered by alphabet from Wuhan University;
(2) Wenchao Ma, equal contributions, ordered by alphabet from Pennsylvania State University;
(3) Quankai Gao, University of Southern California;
(4) Xianwei Zheng, Wuhan University;
(5) Nan Xue, Ant Group (xuenan@ieee.org);
(6) Huijuan Xu, Pennsylvania State University.
:::
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\




